For some people, maintaining good oral hygiene is an overwhelming task. It is why it does not come as a surprise that almost 3.5 billion people have oral diseases, according to the World Health Organisation (WHO). In Australia, the Department of Health said that three out of 10 people do not see their dentist because they believe dental treatments are expensive. One in four children around the age of five to 10 has tooth decay. In adults aged 15 and up, at least one in 25 people have lost all their natural teeth.
Brushing and flossing every day can prevent all these oral health problems. There is always something that you can do today to help improve your teeth and gum health. No matter how small it may be, you can contribute to having healthy teeth for the long term.
This blog post is your ultimate guide in having healthy teeth that look and feel great.
10 Facts You Probably Don’t Know About Your Teeth
First, let us get to know the human teeth more. There are actually a lot of interesting facts about teeth that most people are unaware of.
Here are some of the best ones:
- Toothpaste use has existed since 500 BC. Sure, the toothpaste then cannot be compared to what we have now. In fact, it was mostly a mixture of coral powder and iron rust, which was used by ancient Greeks. Meanwhile, people would use crushed oyster shells, pulverised brick, salt, lemon juice, and ground chalk in other parts of the world.
- Toothbrushes, on the other hand, were made from tree twigs. People would chew on them and use those twigs for cleaning their teeth.
- Your teeth are unique, just like your fingerprint. Even if you have an identical twin, their teeth are not the same as yours. Your tongue also has a distinct print, but that’s another story.
- You can compare your teeth with icebergs since a third of your tooth remains hidden under your gums. Now you see why you should also keep your gums healthy to ensure your teeth get the treatment they deserve. How do you know your gums are healthy? They should be firm and pink in colour.
- You have a total of 32 teeth in your mouth. Count your teeth, and you will find eight incisors (front teeth), eight premolars, 12 molars, and four canine teeth.
- If you think your bone is the hardest part of your body, you’re wrong. The enamel, which is the outermost layer that protects your teeth, is the hardest. It works like a hard shell and is made of phosphate and calcium, which are the same components of bones. However, the enamel is stronger because it is formed by specific crystallites and proteins.
- Having hard teeth though does not mean they are invincible. The enamel, no matter how strong it is, can chip and crack. Decay is a severe problem, which is caused by sugars and acids. Think twice next time you want soft drinks.
- Do you have yellow teeth? Unfortunately, it does not just mean coffee or tea stain; yellow usually means your enamel is partly or even fully decayed. Enamel not only protects your teeth but also helps them stay white. When enamel starts to decay, your teeth will appear yellow, and you could also feel some pain.
- Your mouth is not as clean as you think. If you have plaque, it means you have millions of bacteria in your mouth, consisting of up to 300 different species. One of the biggest culprits is a bacterium known as Streptococcus mutans, which can convert carbs and sugars to acids. These acids can easily destroy the teeth.
- By brushing, you can clean your teeth effectively. However, if you do not floss, you’re missing 40% of your tooth surfaces.
Here at Chelmsford Dental, we recommend that you brush your teeth for two to three minutes. However, did you know that the average person brushes for 45 to 70 seconds? It’s not enough time to clean your teeth, especially with the hundred types of bacteria you harbour in your mouth.
6 Most Common Dental Problems
Now that you know how long you should brush your teeth, it’s time to learn why. By brushing and flossing regularly, you can help prevent the following dental problems that can lead to more serious complications, including heart disease and stroke:
Bad Breath
Halitosis, commonly known as bad breath, is a common issue that affects about one-third of Australians. And 85% of people suffering from chronic bad breath have a dental condition to blame. Often, they have gum disease, oral cancer, and cavities. A mouthwash is a quick solution to this problem. However, it will not cure it. The best way to get rid of bad breath is to visit Chelmsford Dental so that our dentists can rule out any issues.
Cavities
Cavities or tooth decay is one of the most prevalent diseases in the world. According to the University of Adelaide, one in three people aged 15 and over has untreated tooth decay. Cavities happen when plaque combines with starches or sugars, which ultimately attack the enamel.
Gum Disease
Periodontal or gum disease is when the gums are infected. It is one of the top reasons why adults lose their teeth. About 22.9% of Australians have gum disease, which should be taken care of as quickly as possible. Some research showed that heart disease and periodontal disease are linked to each other. If you would like to know more about this topic, please read our blog post about gum disease.
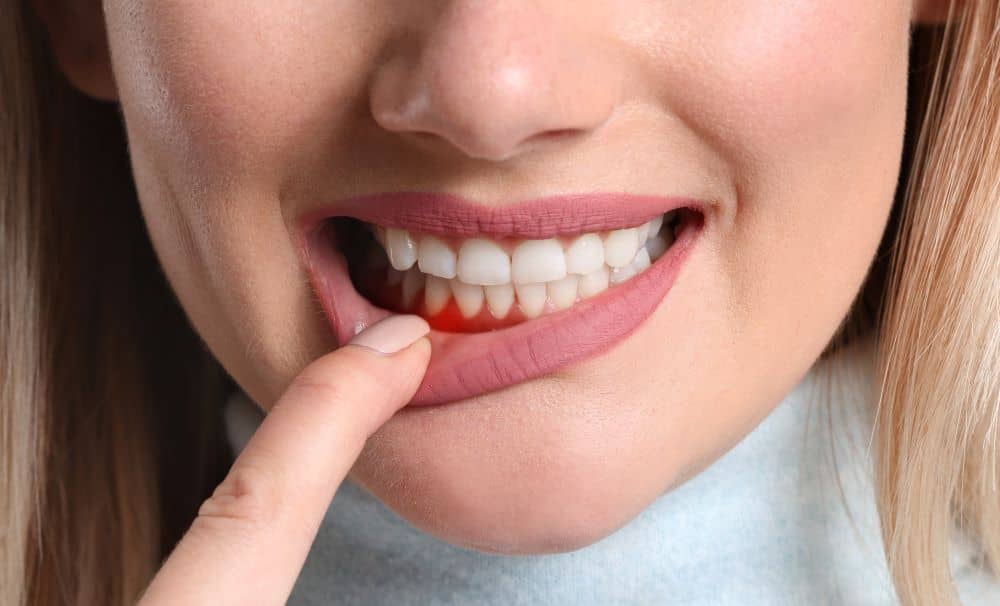

Tooth Erosion
When acid attacks the enamel, tooth erosion can happen. Some people experience severe problems, including tooth cracking, while others only notice increased sensitivity. Dental erosion is a common issue among adults, but it can easily be prevented.
Teeth Grinding
Bruxism or teeth grinding is an issue often caused by stress. About half of the population have this problem from time to time, although five per cent of Australians are forceful and habitual teeth grinders. If you have misaligned teeth, insomnia, and similar sleep issues, you could also start grinding your teeth as you sleep. If you notice that you have loose or cracked teeth, a sore jaw, or a headache when you wake up, it could be due to bruxism.
Oral Cancer
A journal stated that there are about 2,500 new cases of oral cancer in the country every year. It’s a serious disease that can cause death. The Oral Cancer Foundation in the US estimates that one person dies from oral cancer every hour. The good news is that it can be treated, especially when detected early. Age is a risk factor where most people with the disease are over 40 years old.
Your Teeth’s Biggest Enemies: Which is the Worst?
As mentioned above, teeth are protected by a very strong and hard substance called enamel. It serves as the first line of defence, but it can become vulnerable over time. It’s especially true if you don’t brush and floss your teeth regularly and properly.
If you want to keep your natural teeth for a long time, avoid the following:
- Acid: Many people enjoy sodas, fruit juices, and acidic fruits. Unfortunately, they can soften the enamel. Never brush your teeth after enjoying these treats. Your enamel stays vulnerable for about an hour so just rinse with water.
- Chewing: If you have a habit of biting or chewing on pencils, fingernails, and ice, you should stop right now. Your teeth are only designed for breaking down food, not hard things. If you continue to chew on items that are not food, you could end up chipping away the enamel. In severe cases, the tooth can get fractured.
- Harsh Brushing: While brushing helps keep teeth healthy, it can also be bad if you brush too hard. Be gentle to prevent chipping away the enamel of your teeth.
 The biggest enemy of all, however, is sugar. Excess sugar is the main reason for tooth decay as a result of the body’s reaction to sweets. Why is sugar a huge problem for your teeth? Your mouth has a ton of bacteria, which are actually good for your health. However, some are bad, which happen to crave for sugar. When you consume sugar, harmful bacteria get hyperactive, allowing them to produce more acids that can damage your tooth enamel.
The biggest enemy of all, however, is sugar. Excess sugar is the main reason for tooth decay as a result of the body’s reaction to sweets. Why is sugar a huge problem for your teeth? Your mouth has a ton of bacteria, which are actually good for your health. However, some are bad, which happen to crave for sugar. When you consume sugar, harmful bacteria get hyperactive, allowing them to produce more acids that can damage your tooth enamel.
Over time, acids can create cavities or the holes in your teeth. If you do not treat those cavities, bacteria will continue devouring the enamel until they reach the middle of your tooth. When it happens, your dentist may require a tooth extraction procedure.
The best way to ensure bacteria don’t contribute to teeth damage is to consume less sugar while following good oral hygiene. Your teeth are irreparable, but they have the means to defend themselves.
Acids remove valuable materials from the enamel, but your body can enter a remineralisation process. The saliva has minerals needed for remineralisation that allow the mouth to fight off the effects of sugar. This defence is not enough. You need to protect your teeth from bacteria and other problems with proper oral care.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Take Care of Your Teeth and Oral Health
Oral care does not stop at brushing and flossing. You should also eat and drink healthy while getting rid of bad habits. Here are the ways to help ensure your oral health is in its best shape:
1. Floss Your Teeth
Since your toothbrush cannot reach some places in your mouth, you need to floss first.
- Cut about 18 to 24 inches of floss, which should be enough for your entire teeth.
- Curve the floss into a U or C-shape. Then, slide it up and down along each tooth.
- Floss the back parts on all upper and lower teeth.
Flossing can take longer than brushing, but it is necessary. You only have to floss once a day but make sure you go through each section properly. You can use any floss product that you want, including traditional waxed floss and water flosser.
2. Brush Your Teeth
- Use fluoride toothpaste to strengthen your teeth. A pea-sized amount should suffice.
- Place the toothbrush at a 45-degree angle. Keep in mind to brush your teeth and gums very gently.
- Move the toothbrush back and forth in strokes as wide as each tooth.
- Brush both the inside and outside surfaces of your teeth. Don’t forget the chewing surfaces, as well.
- The tip of the brush can be used in cleaning the inside surfaces of your front teeth. Again, use upward and downward motions when brushing.
- Your teeth and gums are not the only ones that need cleaning. Be sure to brush your tongue, too, which will remove bacteria. It also helps prevent bad breath.
- Don’t rinse with water. Just spit the toothpaste out to keep the fluoride in the mouth.
Brushing your teeth should be done twice a day for at least two minutes. Don’t be in a hurry since you could end up cleaning for less than the recommended duration and even cause bleeding. You should also choose a toothbrush with soft bristles, which you should replace every three months. If you’ve had a cold, it is time to replace it since germs can stay in the brush for a long time.
3. Use Mouthwash
Mouth rinses are not required, but they can give your mouth added protection. You may want to use mouthwash when you do not brush your teeth. For example, if you brush morning and night, you can use a mouthwash after lunch. That way, you do not rinse out the fluoride you get from your toothpaste.
Mouth rinses can be antimicrobial, which reduce bacteria and plaque that cause gum disease. Meanwhile, you can also look for fluoride mouthwashes to prevent tooth decay. Fluoride products are not recommended for everyone. For kids six and below, fluoride rinses should not be used to avoid swallowing the product. Make sure you read the label for specific directions.
4. Eat Healthy Foods
Reduce your sugar consumption since bacteria and germs love to feed on it. Acidic foods and drinks, such as soft drinks and coffee, as well as oranges and lemons, can slowly wear away the teeth’s enamel. Instead, eat more crunchy fruits and vegetables, especially young kids. Mushy foods, including processed ones, will not encourage their jaws to work.
5. Drink Water
Decrease the sweetened drinks you usually consume per day. Instead, drink water, especially after eating sugary and acidic foods. Water can help prevent bacteria from sticking on the surfaces of your teeth. Also, dry mouth can lead to bad breath, so make sure you have ample water. The standard to follow is two litres or eight cups for women and 2.6 litres or 10 cups for men per day.
The last but certainly not the least important step is to visit a dentist regularly. A trip to Chelmsford Dental once or twice a year is crucial for routine cleaning and check-up. A dentist will see if you have cavities and help treat the problem. If you already have hardened plaque or calculus, a dentist can remove it for you. You can also be more confident that potential issues will be taken care of because you have a professional-looking after your oral health.
How to Locate the Best Dental Team for You
When you’re looking for a dentist in WA, you may want to ask your friends, family, and even your family doctor for recommendations. Dentists play an essential role in your oral health. Your relationship with them will be for the long-term, which is why you should find someone you’re most comfortable with.
To start your search, here are some questions you may want to answer first:
- What is the most convenient time in my schedule for a dental visit?
- What is the dental practice’s office hours?
- Is the location easy to get to from home, school, or work?
- Where did the dentist receive education and training?
- What about the payments?
- Does the dentist have other professional qualifications?
With the Internet, you can easily schedule regular dental appointments, not only for you but the whole family. Dental check-ups are necessary for everyone, including toddlers, especially those whose permanent teeth are erupting.
Chelmsford Dental is highly experienced when it comes to dealing with both adults and children. We have a great team whose primary goal is to make all patients comfortable. We want to become your lifetime partner in taking care of your teeth. Our dentists and nurses are not just here to provide cleaning services. We also educate patients on how they can improve their oral hygiene.
During a dental check-up, patients can have different treatments. Some may require a fluoride treatment, dental sealant, or even further examination.
Oral health deteriorates over time. Some of the biggest culprits, aside from sugar, are tobacco and alcohol consumption. Therefore, while there is still time, Australians should visit their dentist and listen to the advice given to them. Together with good oral hygiene, routine dental check-ups not only treat dental issues but prevent serious ones, as well.
Do you need a dentist for your child or yourself? Don’t hesitate to contact Chelmsford Dental’s friendly staff. We’ve also made online booking easier. Schedule your appointment today.






